The Endocannabinoid System and its role inside of our bodies.

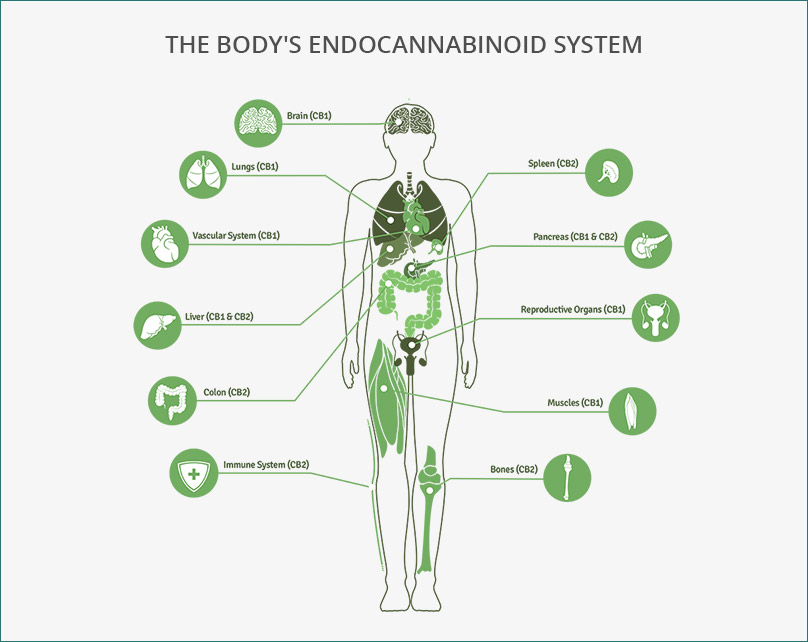
Same as every system in your body, you are born with your endocannabinoid system and you die with your endocannabinoid system. It is there with you your entire life, working all throughout your body. Having a healthy functioning endocannabinoid system is crucial for homeostasis and stability.
Our endocannabinoid systems (ECS) play extremely significant roles within our bodies, much more than just interacting with cannabis. Inside of your brain is a whole system, affecting every other system of your body, that is named after marijuana. Its name was created from the word cannabinoids, which were discovered before the endocannabinoid system. Endocannabinoids are cannabis-like substances that occur naturally within our bodies. Our endocannabinoid system is made up of three parts:
- Endocannabinoids
- Receptors in the central nervous system (CNS) and around the body which bond with the endocannabinoids and cannabinoids.
- Enzymes that help break down endocannabinoids and cannabinoids.
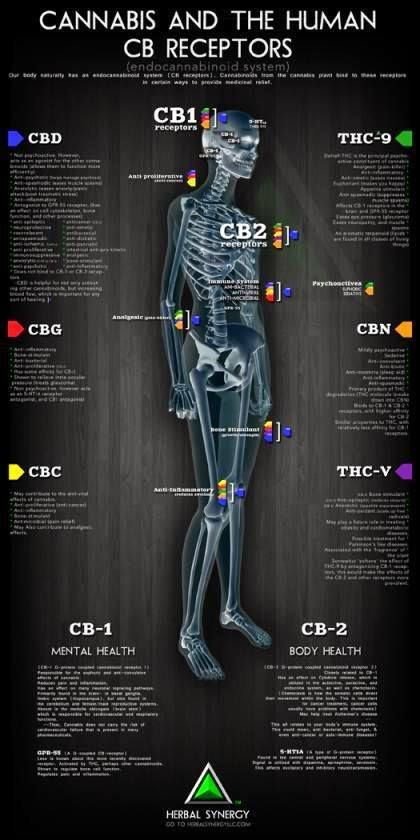
As I mentioned above, the endocannabinoid system is crucial for homeostasis. Homeostasis is your body’s natural balance of health, keeping your internal environment stable and optimal despite your environment externally. Your body works hard, continuously monitoring important levels and functions such as respiratory, circulation, digestion, temperature, etc. When a system is operating outside of homeostasis, your body then activates the endocannabinoid system to help correct it. To correct it, the endocannabinoid system sends signals throughout your body to remind you to eat, drink water, rest, to sweat when you need to cool down, and so much more.
The endocannabinoid system is able to do this through cannabinoid receptors found in select tissues.
We have at least two types of cannabinoid receptors:
- CB1-CNS (brain and nerves of the spinal cord)
- CB2-Peripheral Nervous System (nerves in your extremities), the digestive system, and specialized cells in the immune system.
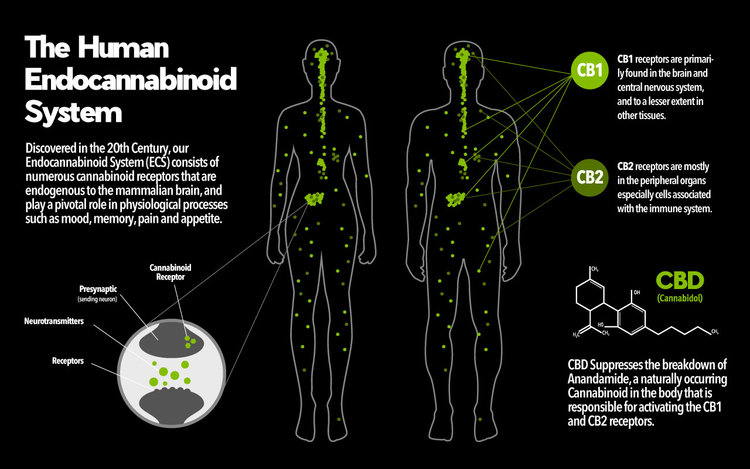
Cannabinoid receptors are believed to be among the most plentiful in our central nervous system, and some researchers hypothesize that we could have a third, undiscovered one, as well.
Through those receptors, the endocannabinoid system helps regulate a lot of important functions such as appetite, digestion, immune function, inflammation, neuroinflammation, mood, sleep, reproductive/fertility, motor control, temperature regulation, memory, pain, and pleasure/reward.
The endocannabinoid system is activated by your body with precision so that it impacts only what it needs to. Once the endocannabinoids have done their job bringing things back into balance, certain enzymes come along to break them down and prevent them from going too far and upsetting the balance in the opposite direction. As you can see, it is a precise response.
That is different than what would happen if someone is recreationally smoking marijuana. They flood their system with cannabinoids, then the drug has a wide range of impacts on physiology, some of which may be beneficial while others may be potentially harmful.

Homeostasis is essential to our health and survival, so when the endocannabinoid system isn’t working properly, a lot of issues arise and cause upset within the body.
Cannabis products stimulate the activity of the endocannabinoid system. Because of this research is going on around the world targeting cannabinoids for potential treatments. This will help to gain a better understanding of the system and the substances. Changes in legal status have also been a driving force for research.
When someone consumes cannabis, a cannabinoid from the plant attaches to the CB1 receptor in the brain and creates a high. This cannabinoid is called THC, tetrahydrocannabinol. One of our body’s own endocannabinoid that attaches to the same receptor is called anandamide.
THC and anandamide are similar, but anandamide doesn’t get you high like THC. Anandamide does have a calming effect, and it gets its name from Ananda, the Sanskrit word for bliss.
The reason anandamide doesn’t get you high like THC does lie with something called the FAAH enzyme, whose job is to break down anandamide and other endocannabinoids. The FAAH enzyme works quickly on the ones your body creates, but it can’t break down THC, so THC stays in your system longer and due to that has a much greater effect.
In your brain, cannabinoids and endocannabinoids work as neurotransmitters (chemical messengers that deliver information from one cell to the next.)
Neurotransmitters all interact with a lot of different receptors and thus have a lot of different effects.
Cannabidiol, CBD, has gotten a lot of attention from researchers because it’s non-psychoactive and you get all of the benefits health-wise without the high that THC provokes. One known function of CBD in the brain is to stop the FAAH enzyme from breaking down anandamide, so the anandamide can have more of an impact. That’s believed to be why CBD has a great effect in treating anxiety disorders.

As medical science has learned more about the endocannabinoid system, discoveries show several conditions that appear to be related to dysregulation of the system, which is called clinical endocannabinoid deficiency (CECD). This still hasn’t been approved as an official condition, but probably will be soon as more studies continue. CECD is implicated in a spectrum of disorders. With unbalanced cannabinoid levels, our bodies do not react positively. CECD isn’t a disease itself but is an umbrella term encompassing conditions with this common feature of affecting more than one system of the body.
Migraines are actually helped by the endocannabinoid anandamide, with its significant effects on pain regulation and serotonin transmission it actively helps sufferers of migraines get relief. Since we know that THC mimics the shape of anandamide and therefore may reproduce its therapeutic effects.
Of course, this is all still being studied but the clinical endocannabinoid deficiency conditions include fibromyalgia, migraines, and IBS. These conditions tend to be resistant to most treatments so researchers are turning to cannabis-based treatments. These conditions also generally involve more than one system, which makes sense when you look at the areas influenced by the endocannabinoid system. Studies are still in the early process of figuring out how to correct endocannabinoid deficiency, but the increasing availability of medical marijuana and CBD products have been largely embraced by the patient community and we are likely to see a lot more research in that area, especially as laws are lifted.

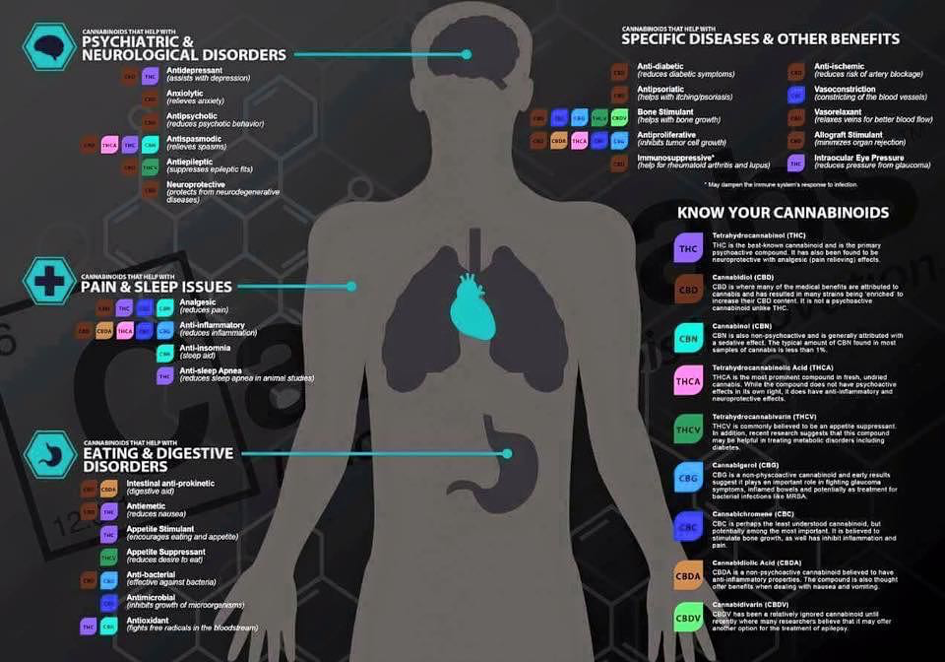
Cannabinoids are being researched as potential treatments for all kinds of conditions, not just those involving endocannabinoid deficiency.
Some of the illnesses that cannabinoids are being researched for include Alzheimer’s, cardiovascular disease, neurological, neurodegenerative, neurodevelopmental, and psychiatric illnesses, acute and chronic kidney disease, autoimmune diseases, chronic inflammatory diseases, and chronic pain conditions.
CBD is already in use for pediatric epilepsy, pain, inflammation, acne, asthma, and a host of other conditions.
Certainly, cannabinoids appear to hold a lot of promise as treatments for a wide range of ailments. It’s great that hemp products are now legal, which opens up treatment options for a lot of people. It can also speed up medical research on CBD as well as eventually drive down the prices.
For more information, please visit us at thesteelcitycbd.com or email us at thesteelcitycbd@gmail.com.