Flavonoids are the lesser-known and lesser-studied compounds in cannabis and part of the entourage effect.
Flavonoids are pharmacologically active compounds known for their antioxidant and anti-inflammatory benefits. They are the largest nutrient family known to scientists with over 6,000 already identified. However, flavonoids are the most understudied compounds found in the cannabis plant. Flavonoids account for roughly 10% of bioactive compounds discovered in cannabis with around 20 or so varieties existing in the cannabis plant.
Flavonoids affect the pigmentation of cannabis plants and are responsible for the colors found in fruits, vegetables, and flowers. For example, anthoxanthins and anthocyanins are what give deep purple cannabis plants their beautiful color. Not only do they provide color, but they are also responsible for protecting plants against elements such as extreme UV rays, pests, parasites, and diseases.
Flavonoids are what give cannabis its character. They provide distinguishing qualities to differentiate between strain varieties. The odor and flavor are in cannabis due to the synergistic qualities terpenes and flavonoids share with one another.
Cannaflavins are the only flavonoids exclusive to the cannabis plant. Preliminary research indicates the medicinal benefits of cananflavins. There are other flavonoids found within the cannabis plant that aren’t exclusive to cannabis alone and can be found in other plants as well.
Let’s talk about the flavonoids found within the cannabis plant, how they work with other components of the plants, and what their medical benefits are.
Since Cannaflavins are exclusive to cannabis, that sounds like the perfect place to start:
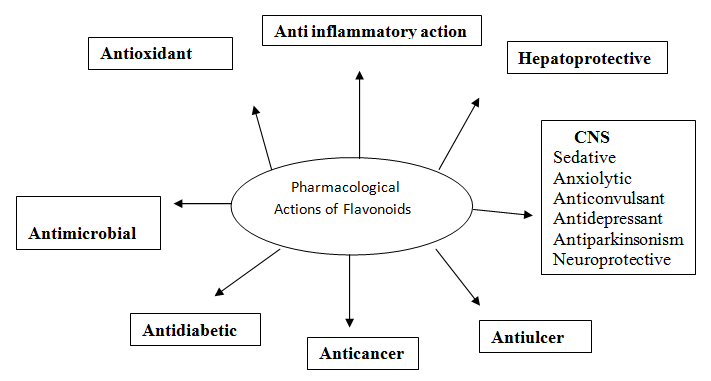
- Cannaflavins A, B & C: Cannaflavin A is pharmacologically active, with anti-inflammatory properties stronger than your traditional NSAID or Aspirin. Cannaflavins B and C are being studied for potential medical benefits. Cannaflavin A and B are two novel prenylated flavones, isolated from the cannabinoid free ethanologic extract of cannabis Sativa L. Both compounds inhibit prostaglandin E2 production by the human rheumatoid synovial cells in culture. These flavonoids contain unique elements beneficial to users. Cannaflavins A, B, and C are similar to THC which has 20 times the anti-inflammatory properties of Aspirin.
- Orientin: Orientin is found in cannabis as well as teas (specifically rooibos) and is a very powerful antioxidant and free radical scavenger, powerful enough to reduce radiation damage.
- Quercetin: Quercetin is one of those that is found in so many other plants as well and hosts a long list of medical benefits. Quercetin aids in better longevity, endurance, healthy heart, immune system support, anti-cancer properties, and is the most abundant and powerful antioxidant. Quercetin also helps allergies, fights chronic fatigue, relieves symptoms related to autoimmune disorders, slows the aging process, and also regulates immune systems response to outside stressors through cell signaling pathways called kinases and phosphatases. Quercetin is a popular supplement and the common oral dose is 500 mg once or twice a day. Quercetin also helps with dermatitis, hives, lower effects of seasonal and food allergies, asthma, and skin reactors. Quercetin stabilizes the release of histamines from certain immune cells. Quercetin helps relieve bladder pain and infections, carrying oxygen and nutrients to muscle and joint tissue. It also holds chemo-preventative activity and has unique anti-proliferate effects on cancerous cells. Quercetin also protects skin cells.
- Silymarin: Silymarin is a powerful flavonoid found in cannabis and milk thistle. It can help reduce damage from free radicals and battle cancer thanks to its powerful antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects.
- Kaempferol: This flavonoid is found in a variety of plants, not just cannabis. It has properties to help reduce oxidative stress and even reduce the risk of various cancers.
- Apigenin: Used in the treatment and prevention of breast cancer. Apigenin is a natural ligand with enormous anti-angiogenic and anti-tumor potential.
- Myricetin: Myricetin is a member of the flavonoid class of polyphenolic compounds. Myricetin has antioxidant, antiviral, antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory and anti-allergen properties. When used with Quercetin, myricetin, and chlorogenic acid as a composition for treating diabetes and metabolic disorders. Myricetin is found in fruits, vegetables, teas, berries, and red wine. It also ameliorates insulin resistance and can execute functions as anti-inflammation, anti-oxidative stress, and anti-hyperlipidemia. Myricetin also has cryoprotective effects such as anti-carcinogenic action, antiviral and antimicrobial properties, and anti-platelet activities. Myricetin is a hypoglycemic component from plant sources.
- Catechin: Catechin is another flavonoid that is an antioxidant. It provides cardiovascular benefits and is found in cocoa, tea, and pome fruits.
- Oritin: Flaven-3-ol, type of flavonoid. It is a component of the proteracacinidin tannins of Acacia galpinii.
- Luteolin: Luteolin is a naturally occurring flavonoid with antioxidant, anti-inflammatory apoptosis-inducing and chemoprotective activities. Luteolin scavenges free radicals, protecting cells from ROS-reactive oxygen species- induced damage and induces direct cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in tumor cells. This inhibits tumor cell proliferation and suppresses metastasis.
- Isovitexin: Isovitexin is a flavone found in cannabis and also passionflower and acai palm. Vitexin is an antioxidant, anti-cancer, anti-inflammatory, and antihyperalgesic with neuroprotective effects.
- B-Sisterol: Beta-sisterol is a nonglucoside. It improves urinary symptoms and flow measures. It also enhances sexual activity. Beta-sisterol eases menopause symptoms, reduces pain and swelling after running, and treats wounds and burns. It is added to some margarines and designed for use as part of a cholesterol-lowering diet and preventing heart disease.
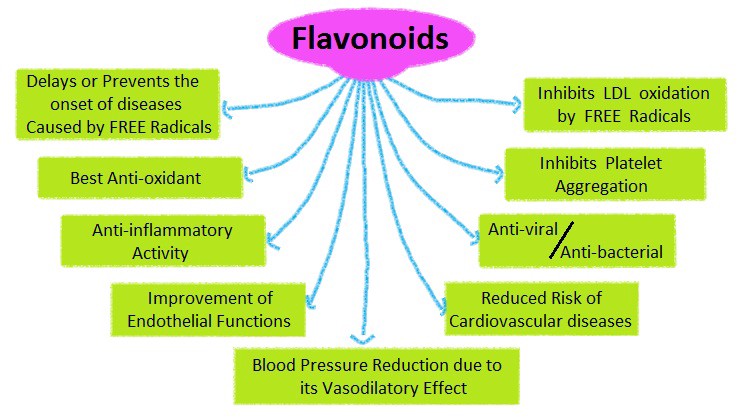
Many properties in cannabis are synergistic. CBD and THC perform best for pain-relief and healing disease when they are used together. This is similar when you consider the terpenes and flavonoids, which are also part of the cannabis make-up. The entire plant is designed to work as a whole to produce the best effects.
Although they are the most understudied component of the cannabis plant, clinical findings have been promising. However, further research is needed to fully understand what role flavonoids play in the overall therapeutic effects of cannabis treatment, especially how they interact with cannabinoids by either synergistically enhancing them or reducing their effects.
Flavonoids are synergistic in cannabis. The ‘Entourage Effect” is the popular, widely used term that describes the synergistic nature of many pharmacologically active compounds in cannabis. Everyone’s body is equipped with an endocannabinoid system, a vast network of receptors that cover almost every organ and system within our bodies. Cannabinoids bind to these receptors to produce different effects, which are further influenced by terpenes and cannabinoids. Specific combinations of these biomolecules have different effects due to the synergistic properties of these various compounds. CBD modulates the effects of THC at the blood-brain barrier. Flavonoids are thought to have similar synergistic abilities. Whether they enhance the properties of cannabinoids or modulate their efficacy is not fully known and requires more research. Flavonoids are incredibly understudied due to strict federal roadblocks that prevent cannabis research at large. In order to better understand the role that cannabis flavonoids play, it is important for federal actions to be lifted in the US to allow for further research to take place. It is imperative for researchers abroad to continue to uncover new discoveries in chemical profiling, allowing us to better understand the complex mysteries of cannabis.
Whole plant extractions typically include CBD, THC, and more than 400 trace compounds. Many interact synergistically to create the entourage effect that magnifies the therapeutic benefits of the plant’s individual components so that the medicinal impact of the whole plant is greater than the sum of its parts.
For more information please visit thesteelcitycbd.com or email us at thesteelcitycbd@gmail.com.